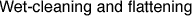

 |
 |
Wet cleaning refers to cleaning with liquids such
as deionized water, weak alkaline water, warm water,
etc, according to the material. This method washes
out harmful metal ions and acids in the paper, and also improves
the whiteness and flexibility of the paper.
Flattening uses water, alcohol, etc., to return paper to its original
flat condition.
|  |
 |
 |

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Testing water-resistance before treatment with
water or alcohol |
|
|
|
|
| Washing out acids or other harmful substances in the paper |
|
|
| Flattening (using suction table) |
|
|
|
 |
 |
•Deionized water
Water that has had all impurities, metal ions, etc., removed. Pure water. |
•Weak alkaline water
Pure water with added magnesium and calcium. |
•Metal ion
Iron or copper ions that can damage paper. |
|
|
|
 |